skg.pow¶
Power fit with additive bias of the form 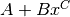 .
.
As a general rule, pow_fit(x, y, ...) is equivalent to
exp_fit(log(x), y, ...) since
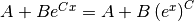 .
.
Todo
Add proper handling of colinear inputs (and other singular matrix cases).
Todo
Add tests.
Todo
Add nan_policy argument.
Functions
model(x, a, b, c) |
Compute 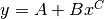 . . |
pow_fit(x, y[, sorted]) |
Power fit of the form 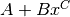 . . |
-
skg.pow.model(x, a, b, c)[source]¶ Compute
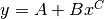 .
.Parameters: Returns: y – An array of the same shape as x, containing the model computed for the given parameters.
Return type: array-like
-
skg.pow.pow_fit(x, y, sorted=True)[source]¶ Power fit of the form
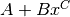 .
.This implementation is based on the approximate solution to integral equation (22), presented in Régressions et équations intégrales. A power fit is regarded as an exponential fit with a logarithmically scaled x-axis in this algorightm.
Parameters: - x (array-like) – The x-values of the data points. The fit will be performed on a raveled version of this array. All elements must be positive.
- y (array-like) – The y-values of the data points corresponding to x. Must be the same size as x. The fit will be performed on a raveled version of this array.
- sorted (bool) – Set to True if x is already monotonically increasing or decreasing. If False, x will be sorted into increasing order, and y will be sorted along with it.
Returns: a, b, c – A three-element array containing the estimated additive and multiplicative biases and power, in that order.
Return type: References